Relative Size in Contrast in Contrast to Absolute Size in Art
A
Abstruse| A spectrum of simplification in comparing to a representational paradigm. Objects can be slightly simplified (generally representational), or extremely simplified (almost unrecognizable), or anywhere in-betwixt the 2 extremes.

Achromatic Value | Values that are created by using only blacks, whites, and greys. "A" + "chroma" = no color.

Actual Lines | Drawn, painted, printed etc. lines which describe actual contours, shapes, forms, and spaces. (as opposed to "implied lines" - see below)
Additive Colour | Color that is created by mixing together the calorie-free of ii or more than unlike colors to create other colors.
(From Wikipedia:) Estimator monitors and televisions are the near common examples of additive color. Examination with a sufficiently powerful magnifying lens will reveal that each pixel in CRT, LCD and most other types of colour video displays is composed of cerise, green and blue sub-pixels, the low-cal from which combines in various proportions to produce all the other colors as well as white and shades of gray. The colored sub-pixels exercise not overlap on the screen, only when viewed from a normal distance they overlap and blend on the heart's retina, producing the same result every bit external superimposition.

Aeriform (Atmospheric) Perspective | The influence of earth'south temper and atmospheric conditions to influence our perception of objects in the distance. Every bit objects get further from the viewer (and closer to the horizon) they ordinarily appear lighter in value, less detailed (softer edges), cooler in temperature, and showroom lower value contrast.

Alignment | A principle of blueprint comprised of lining up the superlative, bottom, sides, or middle of two or more elements on the folio, canvass, wall, etc.. Note the alignment of windows vertically and horizontally in the building below.

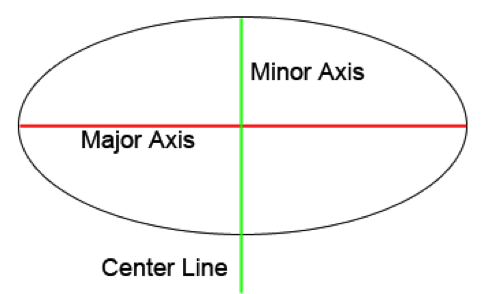
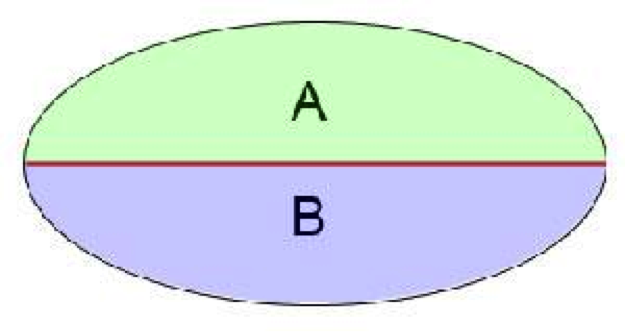
Centrality | A directly line that evenly divides the major and minor space divisions of ellipses.
B
Background | The surface area uttermost from the viewer in a piece of art that depicts depth, or the space/value behind the dominant shapes equally in graphic design. [foreground, middle ground, mountain]. 
Remainder | A visual sensation that the art is equally weighted compositionally. Information technology tin can exist achieved using the placement and amounts of value, shape, line, texture, and colour.

Bleed | The extension of artwork that is across the actual dimensions of the slice. Used to avoid white showing on the edges of the impress should it exist misaligned when cut to size. 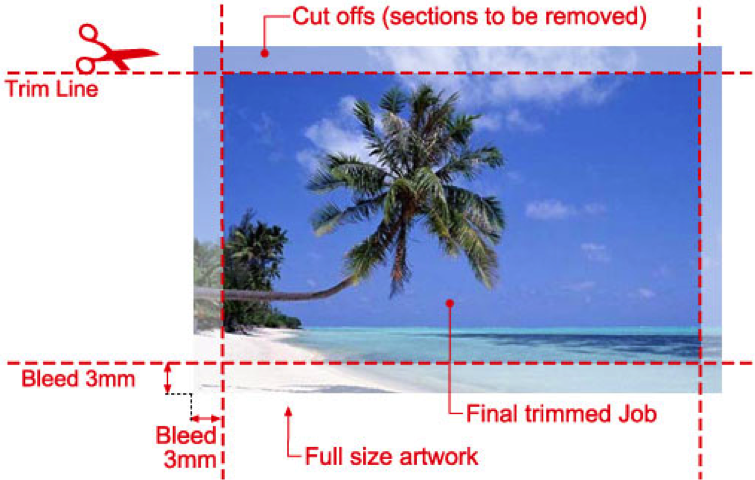
Broken Line | Line composed of actual line combined with implied line (meet actual line definition in a higher place and implied line definition below). A dashed line is a type of cleaved line.
C
Calligraphic Line | Lines which fluctuate in thickness.
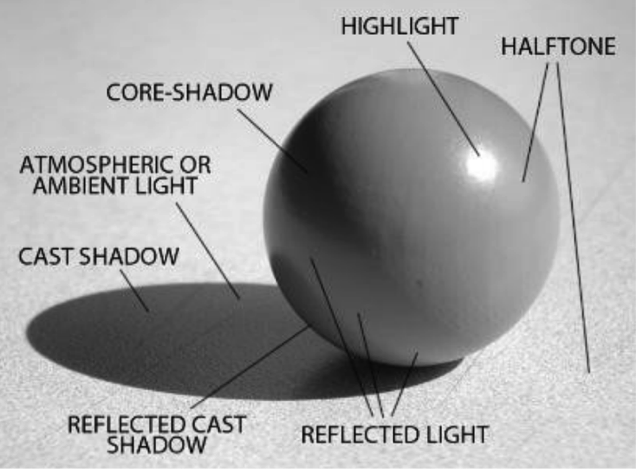
Cast Shadow | The shadow that extends from the core of objects onto other surfaces.


Center Line | A line dividing an object equally through its center.

Center of Interest | The near ascendant part of a piece of artwork, where the eye is drawn to first. Oftentimes referred to as "Master Focal Indicate" too.
Chiaroscuro | Usage of stiff contrast between light and dark. This style became a popular ane during the Renaissance.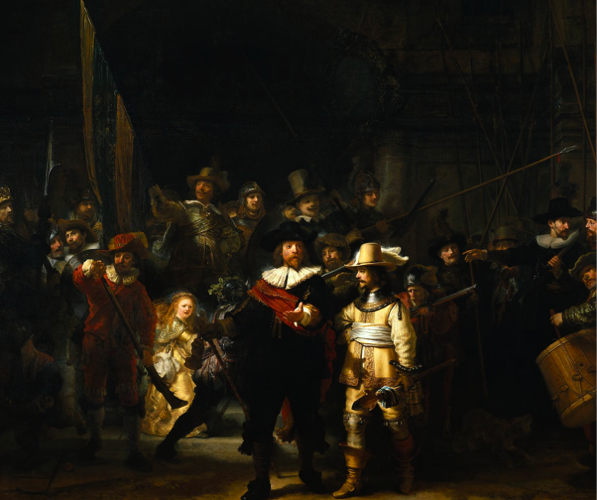 
Chromatic Value Scale | A range of color values, usually organized from dark to low-cal or vise-versa.

Color | The visual spectrum of light—cherry, yellowish, blueish, green, orange, etc.

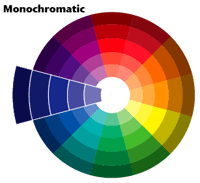
Colour Scheme - Monochromatic | A color scheme limited to variations of one color or hue, with all of that color's tints and shades (values), ranges of temperature, and ranges of saturation or chroma. (Also includes blackness, white, and greys).
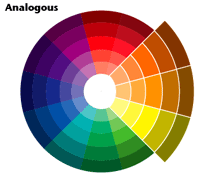
Colour Scheme - Analogous | A color scheme that uses colors that are adjacent to each other on the color cycle.
Color Scheme - Complementary | A color scheme that is based on two colors that are opposite each other on the colour wheel. Note that the discussion is Complementary - non Costless. These two colors complete each other.
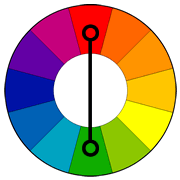
Color Scheme - Separate-Complementary | A color scheme based on one color and the 2 colors that are adjacent to the first color's complement.
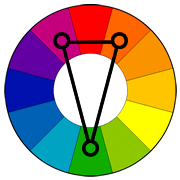
Color Scheme - Triad | A color scheme based on iii colors equally spaced around the color cycle.

Limerick | The terms "limerick" and "pattern" are sometimes used synonymously. Limerick by and large refers to the pictorial arrangements of the elements of design in a slice
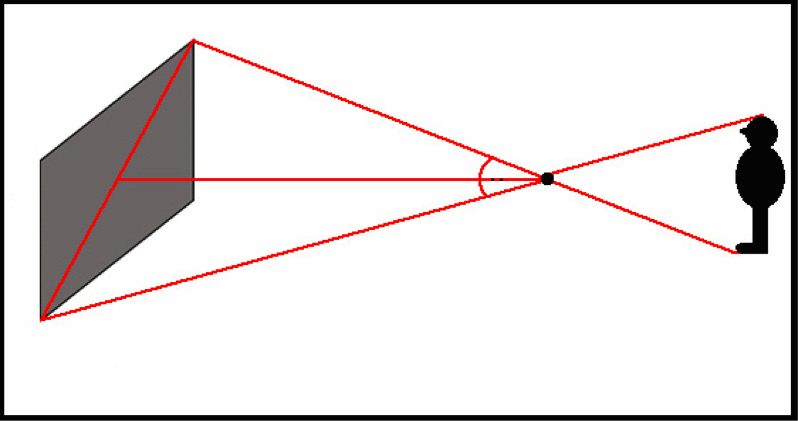
Cone of Vision | People take an estimate lx degree bending of undistorted vision that extends as an imaginary cone from their eyes forrad. Outside of the 60 caste angle, objects brainstorm to be distorted. In linear perspective, it is indicated with a 60 degree angle kickoff at the station bespeak.
Concept | The idea for the creation of a piece of art. Concept involves thinking beyond the size, position, bending, value, texture, etc., of the object.
Construction Drawings | Line artwork that shows the process of drawing objects every bit if they were transparent
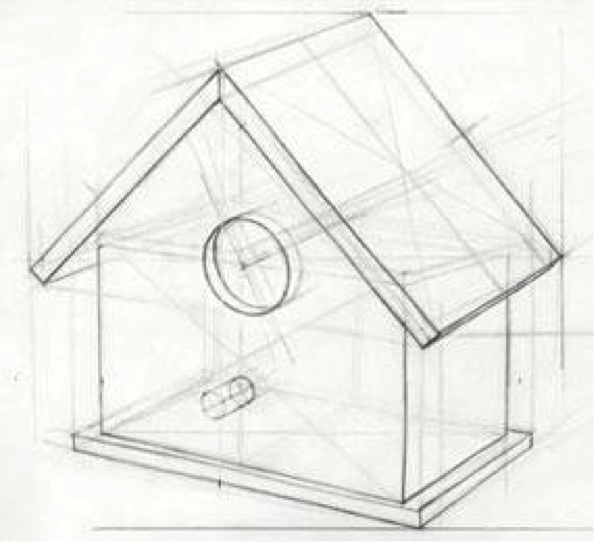
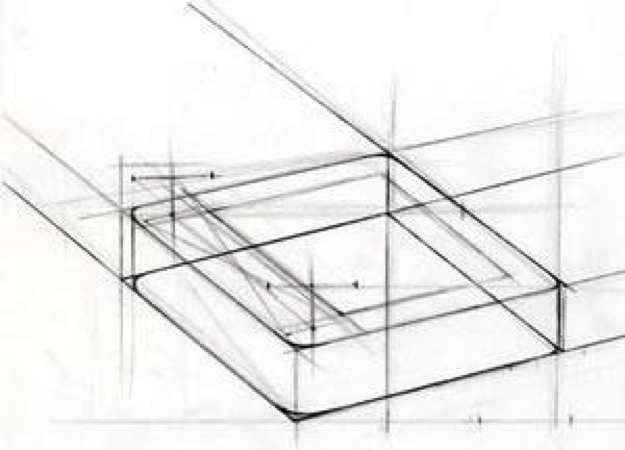
Structure Lines | Lightly drawn lines that are used to develop the proportion, perspective, and shape of objects and compositions.
Content | Is the artist's intended significant or bulletin contained and communicated within a work of art other than its physical tangible backdrop, due east.grand. paint strokes. It includes emotional, intellectual, symbolic, thematic, and narrative connotations.
Continuity | A phenomenon which refers to the pattern past which the eye should travel through an paradigm. A limerick contains continuity if the heart led off the page, but instead is allowed to travel around in the image.
Contour Line | Lines which travel along contours or objects in an image, creating the illusion of dimension.
Contrast | Comparison of variations of line, shape, value, texture, and color.

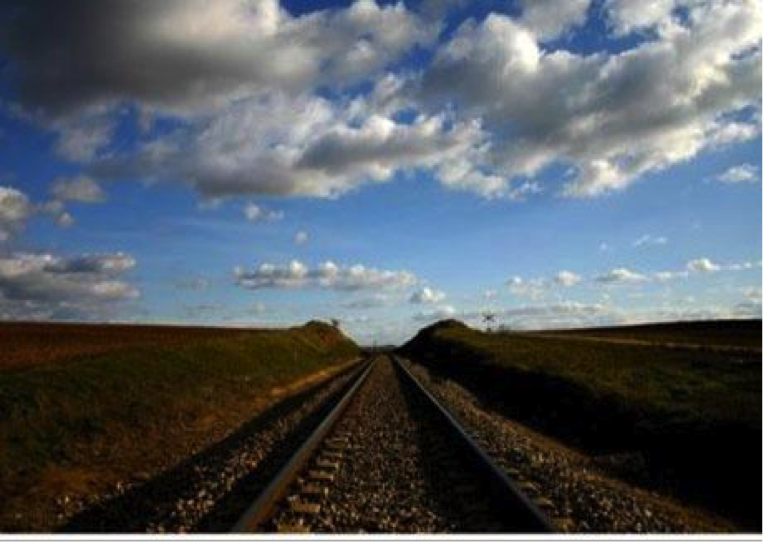
Convergence | The illusion of parallel lines that appear to come together in the distance. The points at which they announced to converge are the vanishing points.

Core "Edge" Shadow | The nighttime "area of light" on an object that begins where the halftone/direct light ends. A core edge and cadre shadow are the aforementioned things, the border only refers to an abrupt aeroplane alter of the object as on a cube, rather than a gradual border equally on a ball.
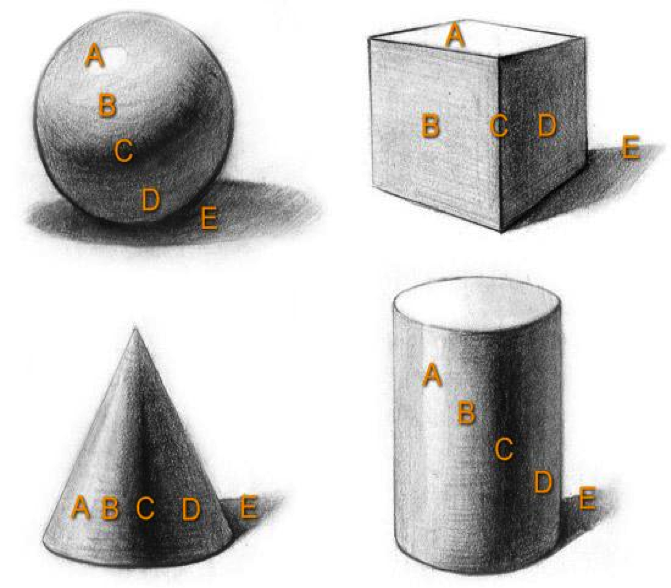
Core Shadow | The dark "area of light" on an object that begins where the halftone/straight light ends. On rounded objects information technology is soft-edged and appears as a ring. On right-angled objects information technology is hard-edged and flat. The shadow marked by "C" represents the core shadow.
Cantankerous-Contour | Drawing technique that uses lines beyond the profile of a grade to create the illusion of dimension. Lines can cross vertically, horizontally, or both.

Cross-hatching | A technique of shading which uses closely spaced parallel lines to create value and effects. Artists use this technique, varying the length, bending, and closeness of the lines to create various furnishings.
Curvilinear | An "organic" shape formed or characterized by curving lines or edges.

D
Depth | In Art, depth is the illusion of distance from foreground toward the background.

Design | The terms "design" and "composition" are sometimes used synonymously. Except in the definition of "graphic blueprint," the term "design" refers by and large to the planning/conceptual intent more than than the arrangement of shapes, values, line, etc. (Elements of design.)

Diagonal Line | A line which diagonally bisects the horizontal plane of vision. Diagonals are used in art to simulate motion or create emphasis.
Diminution | The visual consequence that objects appear to become smaller in the distance.
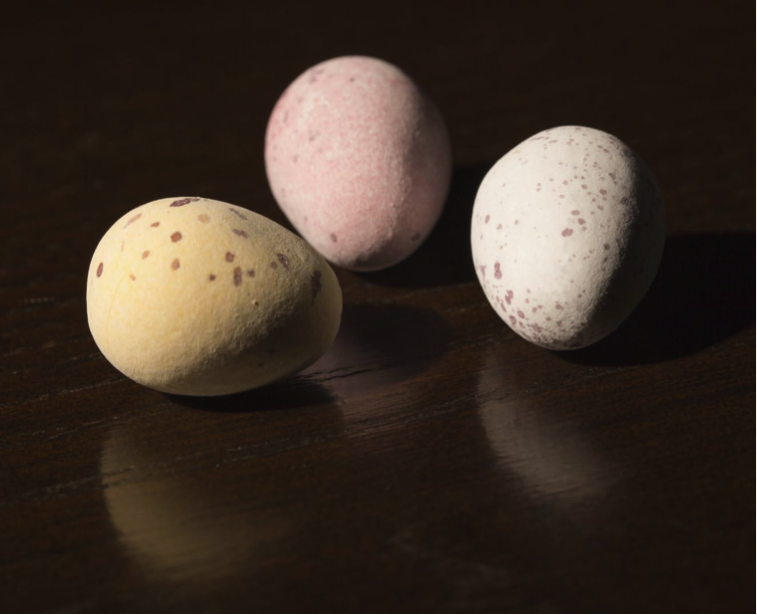
Straight Low-cal | Lighting in which the greater part of the light comes directly from the light source to the area lit. An object in direct light will have a "low-cal side", and a "shadow side". The left side of the eggs below are in direct light.

Dominance | When i of the elements of pattern (east.g. shape, color), is used in a limerick more than whatever of the others. Do not confuse authorization with focal point.
Dry Media | Graphite, charcoal, pastel, etc., used to depict.
Dynamic | Description of a composition, etc. that moves the eye rather apace through the limerick, usually using curved or diagonal lines. This technique is often used to strive for an exciting or energetic feeling to the artwork.
E
Edges-Soft | Gently fatigued marks that are less focused as compared to marks or edges that are sharper focused.
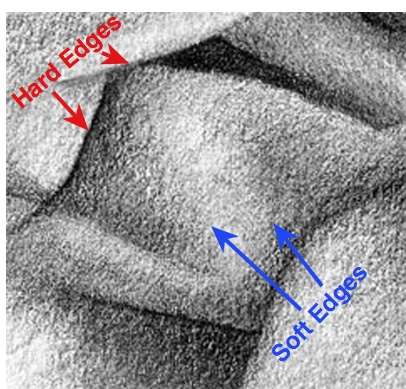
Edges-Difficult | Marks that are drawn in sharper focus as compared to marks or edges that are less focused.
Elements of Design | The most basic ingredients/parts used to compose/design fine art. They are line, shape, value, texture and color in ii-dimensional art (e.g. paintings, drawings, etc.). Three-dimensional art (eastward.g. ceramics, sculpture, etc.) has the added element of space. Film/video has the added chemical element of movement.
Ellipse | An ellipse is a perfect circle that has been foreshortened into perspective. The space above and beneath the major axis is always equal.
Centre Level | Middle level is the actual height at which the viewer's eyes are when looking at an object, an interior scene, or an exterior scene. It is also a reference line, in linear perspective, that extends parallel (left to right) within a format.

F
Five-Value Calibration | A scale of values evenly stepped from white to black.

Floor Plan | Overhead, "bird's center view," diagram used to show placement of shapes/objects—mostly of interiors of buildings.

Focal Point | Focal points are visual expanse(s) that are of the greatest emphasis in the composition. They are created using variations of the elements of blueprint. The focal point is usually the first thing your eyes are drawn to in a motion picture.
Foreshortening | Foreshortening of an object occurs visually when it rotates or turns from the viewer. The result causes its length to appear shorter than information technology actually is. The illusion of foreshortening tin be re-created on a two-dimensional surface past using the principles of linear perspective.

Course | The utilize of the Elements and Principles of Design as well as the physical tangible properties of the fine art (eastward.g. thickness of pigment, paint strokes, proportion, format, etc.).
Format | The measureable pinnacle and width of a drawing, illustration, painting, photo, graphic design, in 2-dimensional art.
Frisket | A masking newspaper or a film that is placed on top of a drawing to shield selective areas from receiving unwanted value during the drawing procedure.
G
Gesture | Lines that imply the suggestion of movement, specially of man or animal forms.
Geometric Shapes | "Geometric shapes" refers to shapes that are 2 dimensional in nature (e.g. circles, squares, ovals, logos, symbols, etc.) equally in graphic blueprint. Also, man-made objects such equally cylinders, cones, cubes, boxes, or combinations of these. The reverse of geometric shapes are organic shapes.

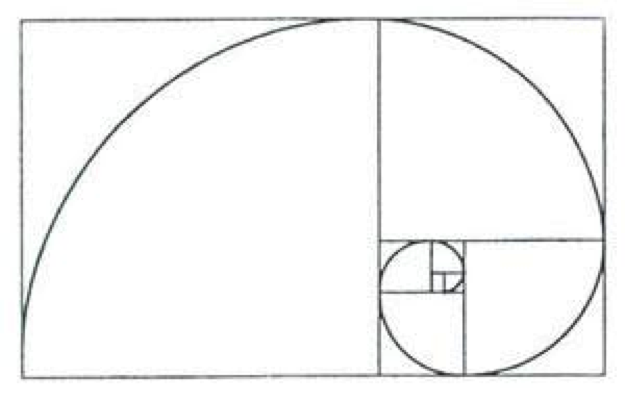
Aureate Section | A mathematical ratio evident in nature. The ratio is .618 to 1; about eight dashes to 13 (--------/-------------) or 2.5 to 3.five. The dominion of thirds is a close approximation of the gold section units.
Gradation | Incremental steps when going from light to dark, neutral to intense, warm to absurd, rough to smooth, etc.

Ground Measuring Line | A linear perspective term. It is used to mensurate foreshortened length (true length) coupled with the vanishing points and measuring points.
H
Half Tone | The full expanse of an object, surface plane, etc. that is illuminated by the dominant light source.
Harmony | When all individual parts of an artwork, ie: elements, principles, objects, colors, values, etc., work together to brand a better whole, the result is said to be in artistic "harmony".
Hierarchy | The deed of placing items in a hierarchy, ie: tallest to shortest, oldest to youngest, etc.. Effective designers determine the importance of every specific element in a limerick, etc. from most important to least important, then give the viewer visual cues to communicate that hierarchy and to create potency and subordination.
High Definition | Images that are characterized by a high level of detail, sharpness, and clarity. (I don't use this term - leftover from Lana(?). Do we keep?) TT
High-Key | When a piece of artwork is created using predominantly lighter values (tin can exist achromatic or chromatic) it is considered a high-keyed composition. High-key compositions can create a "softer", "lighter", or more "peaceful" feeling (simply this is not an absolute rule).

Highlight | The brightest area of light on an object. It is always inside the halftone. Expanse "A" in the picture below.

Horizon Line | Horizon line refers to a physical/visual boundary where the heaven and the state are separated. The term "horizon line" by and large refers to drawings that are outdoors. Information technology is sometimes used synonymously with the term "eye level."

Horizontal | All lines or edges that are parallel to the top or lesser of a two dimensional rectangular format, and/or parallel to the viewer's eye level.
Hue | Synonym of Color - usually inferring the base or actual colour without adding black or white.
I
Implied Lines | A line that is suggested or unsaid rather than really drawn/painted, etc.. The viewer'southward brain connects or completes the shape rather than an bodily line doing so.

Isolation | A separating segregation by contrasting values, patterns, size, color, texture, subject matter, negative shapes, etc.
J
K
L
Lift-out Method | A drawing technique used to create the half-tone and highlights by erasing.
Light and Shadow | A term in fine art referring to the "Areas of Light," due east.one thousand. highlight, halftone, core, reflected light, bandage shadow, reflected cast shadow, mirror image, and atmospheric low-cal.
Light | The term "light" tin have several different meanings, ie: gospel meanings, secular meanings, etc.. As an artistic term, calorie-free follows certain universal rules (for example, it ordinarily can't curve around a corner without a mirror or other help). The human eye and brain, through constant exposure since birth, has learned to translate these lite and shadow patterns into three-dimensional grade. Photographs capture these patterns, which is why photographs appear "realistic". Artists who are capable of replicating these calorie-free and shadow patterns are able to create the illusion of 3-dimensional objects on a ii-dimensional surface (paper, sail, etc.)
Low-cal Bands |
Line of Sight | An imaginary reference line that extends direct frontwards, perpendicular to the viewer's optics. Information technology is whereever the viewer is looking.
Line | One of the 5 elements of design.
Line Quality | A term referring to the visual attributes of a line (difficult/soft, curved/straight, thick/thin, nighttime/light, etc.).
Linear Perspective | A principle in two-dimensional art used to create the illusion of three dimensions / volume and depth. It is based on how we visually perceive the world.
Local Colour | A term referring to the actual color/hue of all things (red, green, orange, bluish, yellow, etc.).
Local Color Value | A term referring to the inherent value of all things due to its color or hue. As an example, the local color value of blue is darker than the local colour value of xanthous.
Lost and Found | A term used to depict an element which "stops" and then "starts again" elsewhere on the page. The viewer'due south eye (brain) fills in the empty infinite, connecting the imaginary or unsaid lines.

Depression Definition | Images that are not sharply defined through the lack of fine item. (I don't apply this term - leftover from Lana. Do we keep?) TT
Low-Central Value | When a piece of artwork is created using predominantly darker values (can be achromatic or chromatic) information technology is considered a low-keyed composition. Depression-central compositions can create a "darker", "ominous", or more "dramatic" feeling (but this is not an absolute rule).

M
Mass |
Measuring Point | A linear perspective term used to measure foreshortened length coupled with the vanishing points and the ground measuring line. It is always located on the heart level.
Mirror Image | The name given to an "Area of Light" for images that are projected onto a reflective surface.
N
Non-representational | Shapes that are not intended to be recognized as representing whatsoever existent object.
Negative Infinite | The subordinate space surrounding ascendant shapes inside a format.
O
One Signal Perspective | A piece of work of art in which all parallel lines converge at a single vanishing point creating the illusion of iii-dimensional space and depth on a two dimensional surface. The vertical and horizontal lines are parallel to the vertical and horizontal sides of the pic plane/format, and the vanishing bespeak is on the eye level.
Organic Shapes | Generally natural objects, such as plants and animals. Organic shapes have lines that are commonly gratis and irregular. The reverse of organic shapes are geometric shapes.

Overlapping | A technique that places one object in forepart of the other, in ii-dimensional fine art, used to create an illusion of depth.

P
Paper Stump | A commercial drawing tool equanimous of tighly rolled paper with the appearance of a pencil. Information technology is used to alloy/smooth dry media, i.e. charcoal, graphite, pastel.
Parallel | Lines, shapes, or edges that are ever the same distance apart and yet appear to converge to a common betoken, i.east. a vanishing point.

Pattern | Regular repetition of an chemical element or elements in a piece of fine art.
Perspective | A set of universally applied cartoon principles that are used to create the illusion of three-dimensional volume and depth onto a two-dimensional surface.
Picture Plane/Format | The working space inside which a ii-dimensional painting, cartoon, illustration, photo, design, etc. is created.
Pitch | The degree of inclination or angle of a aeroplane. The greater the pitch, the narrower the visible expanse. [ready]

Aeroplane | A flat, 2-dimensional surface that can extend vertically and horizontally in whatsoever management. For instance, a cube has six equal planes that are either parallel or intersect/meet each other.
Plumb Line | Horizontal or vertical lines used to determine size, position, and angle of objects.
Positive Shapes | The dominant areas within a piece of work of art. They are normally three-dimensional objects in two-dimensional fine art.
Principles of Blueprint | How one applies the "elements of design" to create fine art. Some principles of blueprint include: residue, harmony, repetition, unity, contrast, variety, dominance, focal point, etc.
Proportion | The relationship/ratios of sizes, positions, and angles of one part to another. An object that is drawn in proportion is an authentic reflection of the ratios of the actual object.
Proximity | The arrangement of shapes that are placed near each other in a format used to create a sense of residual, dominance, focal point, etc.

Psychic Line | Synonym of Implied Line. The encephalon creates a "line" that connects one point to another. For example, when pointing to something, the eye travels from the hand to an object equally if there were a connecting line.

Q
R
Rectilinear | A "mechanical" shape that is formed by using only straight lines.
Reference Signal | A linear perspective term, used to assist in transfer of calibration.
Reflected Bandage Shadow | An "Area of Light" of the cast shadow which is reflected back onto the shadow side of the object.
Reflected Light | An "Area of Light" on the shadow side of an object, illuminated by light billowy onto it from an adjacent halftone. The reflected light is essential to place the core shadow.

Repetition | Is a principle of pattern that repeats elements (line, value, texture, shape, color) to create unity.
Representational | Artworks which depict (replicate) recognizable, visual objects inside the concrete world, such every bit people, places, and things.
Rhythm | A "principle of design" which uses regularity inside an image, such equally pattern, to create the illusion of move.

Rule of Thirds | A general guideline used in the system of focal points within a composition.

S
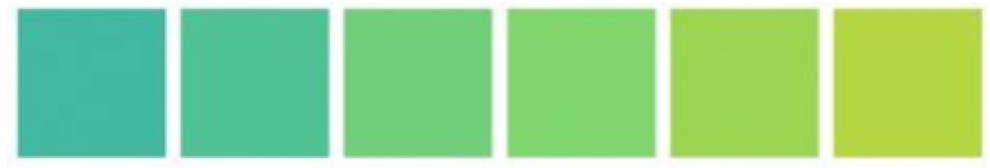
Saturation | The measurable pureness or total forcefulness of a colour in comparing to a grayed version of it. Synonym of Chroma. Run across the saturated (outside) to unsaturated (inside) example below.

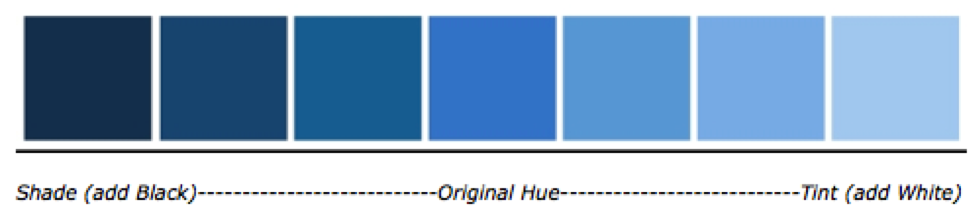
Shades | A new colour that is created by mixing black into an existing color, which makes it darker and less saturated. The opposite of a shade is a tint.
Shape | An "element of pattern" which is a two dimensionally enclosed expanse. They can be either geometric, organic, or a combination of both.

Skyline | A term describing where the heaven meets the mountain, edifice, tree top, etc.
Space | An "element of design" in 3-dimensional art just, i.eastward. sculpture, ceramics. Two-dimensional art creates an illusion of infinite by effectively using the elements and principles of design.
Spider Method | A quick mode to create perspective angles in a 2 point drawing. The perspective angles visually appear like spider webs.
Space | An "chemical element of design" in 3-dimensional art only, i.due east. sculpture, ceramics. 2-dimensional art creates an illusion of space by effectively using the elements and principles of design.
Station Betoken | A linear perspective area that designates the viewer'south or intended viewer's location, in one, two, and three point perspective. It is always placed at the apex of a xc degree angle.
Starburst Method | A quick way to create perspective angles in a 1 point drawing. The perspective angles visually appear similar a starburst.
However Life | A term referring to an arrangement of 3-dimensional objects of which the artist intends to describe or pigment.
Subordinance | When one or more of the "elements of design" are used in a limerick with less accent than any of the others.
Subtractive Color | What nosotros normally retrieve of when combining different colors of pigment, paint, ink, etc.. Every bit colors are combined, they reflect a "new" color dorsum to the viewer'south heart. This is termed "subtractive" because nosotros are subtracting light from the light source.

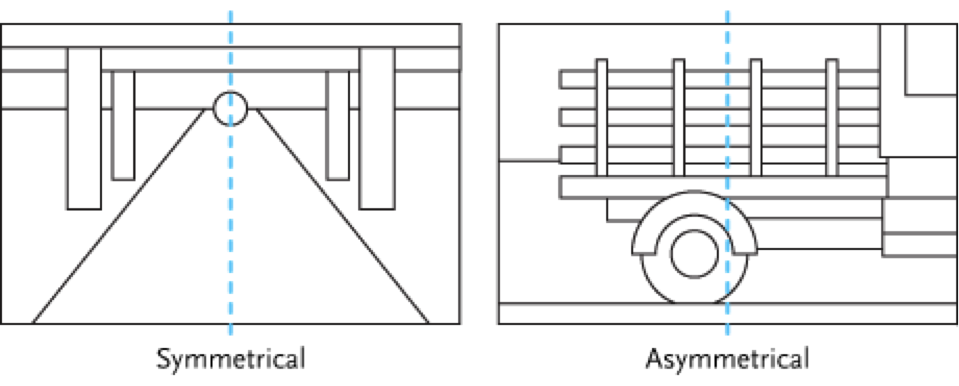
Symmetrical | A visual awareness that the fine art is equally weighted compositionally. It can be accomplished using the placement and amounts of value, shape, line, texture, and color.
T
Tangents | The alignment of edges of objects in a limerick so that they just touch, or nearly bear upon, each other. This makes the pattern visually confusing and irritating.

Temperature | The degree of measurable warmth or coolness of a color in relationship to another color. While nosotros normally recollect of reds, yellows, and oranges as being warm colors, and dejection, greens, and violets as cool colors, temperature is e'er relative. In other words, whether a color is "warm" or "cool" depends upon the other color(s) we are comparison it to.
Texture | An "chemical element of pattern" referring to the illusion of how something feels or how it would expect if touched. It is also the use of non-representational lines, values, and colors to add balance to the composition, such equally paint strokes, cross-hatch marks, etc.

3 Dimensional Shape | Pertaining to the length, width, height, and depth of existent or imagined objects; the illusion of which tin be rendered using linear perspective.
Tints | A new color that is created past mixing white into an existing colour, which makes it lighter and less saturated. The opposite of a tint is a shade.
Tooth | Refers to the surface texture (smoothness or roughness) of paper, illustration lath, sheet, etc.
Transfer of Calibration | The term "scale" in this defintion is synonomous with the term "size" i.eastward. superlative and length (including foreshortened length). It is a way to maintain and record the accurate proportion produced by the visual issue of diminution as an object moves higher up or below the eye level/horizon line, or towards or away from the viewer in a drawing.
Transfer Paper | A slice of paper used to compare lengths or widths on a drawing. It made by roling up a piece of newspaper and flattening information technology.
Truthful Top | A linear perspective term referring to the reference vertical height of an object, which is afterwards used to transfer its scale (forward or backward) within the format.
True Length | A linear perspective term referring to the reference horizontal length of an object, which is subsequently used to transfer its calibration (forrard or backward) within the format.
Two Bespeak Perspective | A piece of work of art used to create the illusion of 3-dimensional infinite and depth in which all parallel lines converge at 2 vanishing points on the horizon or heart level line. Only the vertical lines are parallel to the vertical sides of the moving-picture show plane/format.
Two Dimensional Plane | Flat surface used for creating art, i.e. newspaper, sheet, etc.
U
Unity | The effect when all elements, principles and aspects (grade and content) of an prototype appropriately belong together.
V
Value | Referring to the darkness or lightness of an object or an area, whether the object is in color or black and white. [split up]

Vanishing Betoken | In linear perspective, it is a specifically designated area on the horizon/centre level to which parallel lines converge. VP1 is to the left of the station point/line of sight. VP2 is to the right of the station point/line of sight. VP3 is above or below the horizon line and is at the station point.

Variety | A "principle of design" in which differences, alterations, changes, and contrasts of line, shape, value, texture, colour are shown in artwork.
Vertical Measuring Line | A linear perspective term coupled with vanishing points used to transfer and measure vertical calibration (true top).
Vertical Line | A line that is angled xc degrees/perpendicular to the horizon/heart level or format (bottom or acme).
Visual Gravity | The illusion that shapes appear to accept been or are being affected past the Law of Gravity within a piece of fine art.
Visual Pace | The speed at which the eye moves through the slice of fine art.
Visual Weight | An chemical element, or part of a composition, which commands more than attention in comparing to other elements, or parts. This is commonly achieved using value or color contrast.
Volume | Leon, remind me of Matt's analogy nearly Mass vs. Book? TT
Due west
X
Y
Z
coonrodhapteraind.blogspot.com
Source: https://courses.byui.edu/art110_new/art110/glossary/glossary.html
0 Response to "Relative Size in Contrast in Contrast to Absolute Size in Art"
Post a Comment